Cloaking Inequity: National and Urban NAEP Results: Neighborhood Public Schools 23, Charters 4
With increased attention and resources given by President Donald Trump and Secretary of Education Betty Devos to charter schools as an alternative to neighborhood public schools, it is crucial to analyze whether or not students who attend charter schools actually exhibit better education performance results compared to non-charter neighborhood public school students. While standardized test measures are not the most complete or ideal to analyze student outcomes, they can play a role in analyzing whether or not charter schools do truly deliver better performance for students.
This post utilizes data from the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP). The NAEP is conducted by the National Center for Education Statistics and the U.S. Department of Education. The NAEP was “first administered in 1969 and is the largest continuing and nationally representative assessment of what our nation’s students know and can do in subjects such as mathematics, reading, science, and writing.” Standard administration practices are implemented to provide a common measure of student achievement and is consider “the nation’s report card.”
For this blog post, the NAEP Data Explorer tool was used to compare student performance results at the national and large city level. Composite scale scores were compared for charter schools vs. non-charter neighborhood public schools at the “large cities” level due to the fact that the majority of charters are located in urban areas. We consider the Data Explorer’s publicly available composite reading, mathematics, and science scores for 4th, 8th, and 12th graders over the course of six years (2009-2015). This post includes a school-level analysis due to the fact that the student-level data is not publicly available online (For student-level NAEP data comparisons see for example School Sector and Academic Achievement: A Multilevel Analysis of NAEP Mathematics Data).
Results
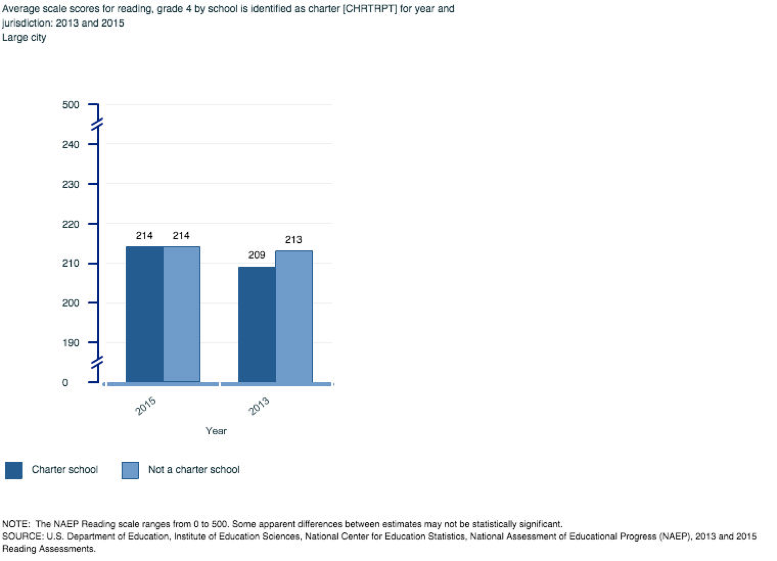
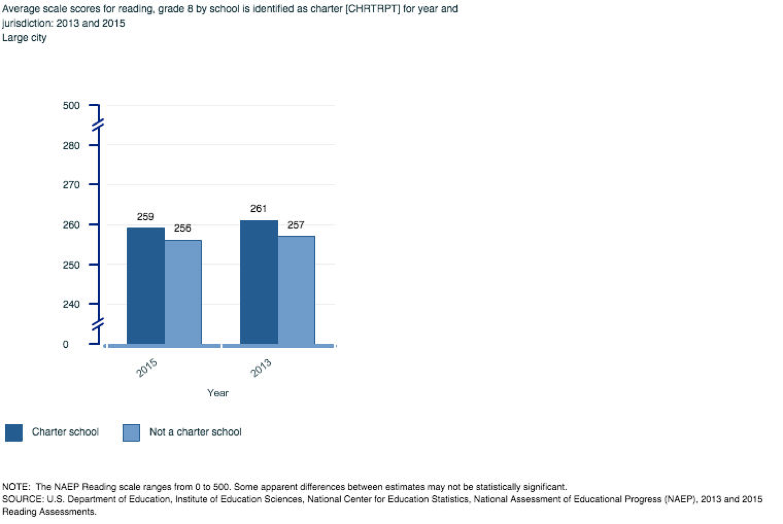
One would most likely suspect from the current positive public discourse about charter schools that they would display higher national and large city NAEP performance when compared non-charter neighborhood schools, however, this is not actually the case when examining achievement data at the school level. Out of the 28 total comparison tests run, only 4 times did charters produce higher composite score averages than non-charter neighborhood public schools— 8th grade reading and math in the years 2013 and 2015. There was a tie in the large city comparison for 4th grade reading in the year 2013 as charter schools and non-charter neighborhood public schools displayed the same average composite scale scores. In the other 23 cases charter schools produced lower average composite scores on the NAEP (math, reading, science) than non-charter neighborhood public schools.
What were the average differences between charters and non-charter neighborhood public schools? Overall, the 18 comparisons utilizing national samples of non-charter neighborhood public schools displayed composite scores 9.3 points higher on average than charter schools. For the ten available comparisons using samples from large cities, non-charter neighborhood public schools displayed composite scores 0.3 points higher on average than charter schools. Thus, the predominant finding is that non-charter neighborhood public schools outperform charters in the NAEP results on average.
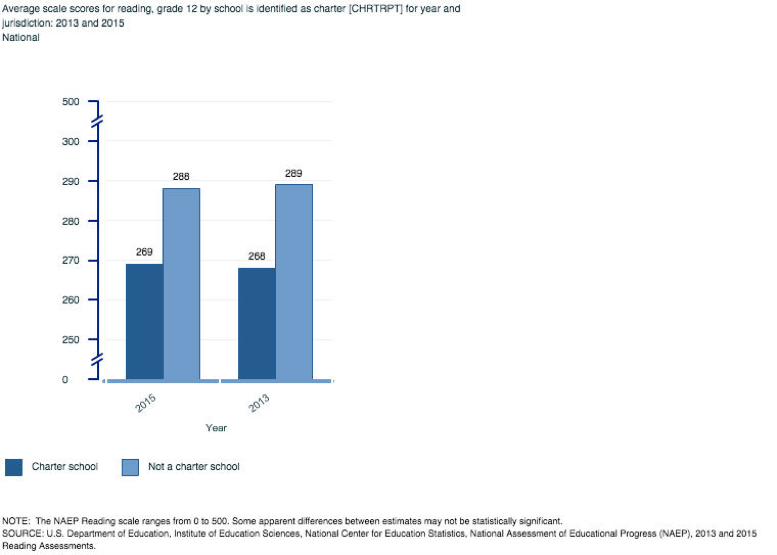
The stark difference in student achievement between charters and non-charters is extraordinarily large in the final year of high school. The national comparisons in the 12th grade show about ~20 point differences favoring non-charter neighborhood public schools in reading, math and science over charters. Of note, the 12th grade comparisons are only at the national level because data for comparisons were not available at time of writing for large cities in the NAEP Data Explorer.
In conclusion, the school-level national and large city NAEP results drawn from the Data Explorer are informative for the public discourse as charter schools are presently being presented as a superior alternative to the public school system. These descriptive school-level results from the NAEP Data Explorer suggest that the relationship between charter schools and improved student performance is not being realized nationally and in large cities. As a result, the present conversations promoting outstanding overall success of charter schools clearly need to be reconsidered and reframed.
4th Grade Composite Score Comparisons (National and Large City)
Mathematics


Reading

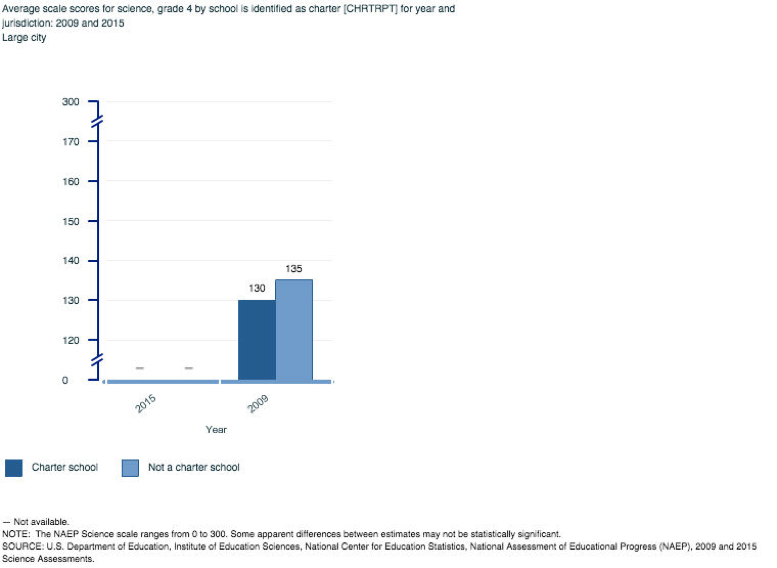
Science

8th Grade Composite Score Comparisons (National and Large City)
Mathematics


Reading

Science


12th Grade Composite Score Comparisons (National)
Mathematics

Reading
Science

These analyses were written in collaboration with Brent Clark Jr., 2017 Sacramento State Pathways Fellow.
Note: We are aware from recent personal conversations in DC that NAEP will soon release a charter school study.
This blog post has been shared by permission from the author.
Readers wishing to comment on the content are encouraged to do so via the link to the original post.
Find the original post here:
The views expressed by the blogger are not necessarily those of NEPC.

